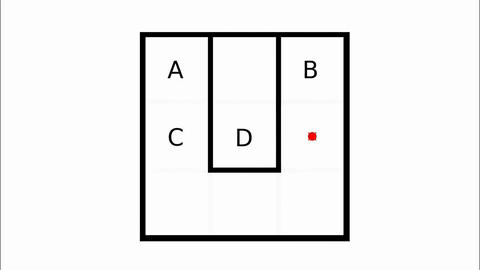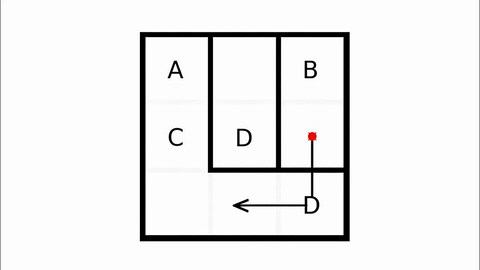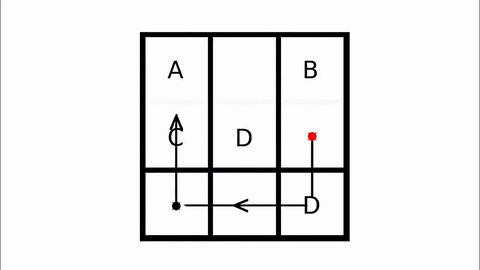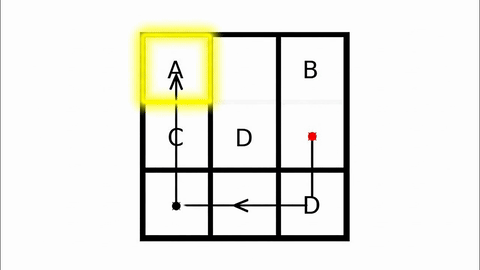
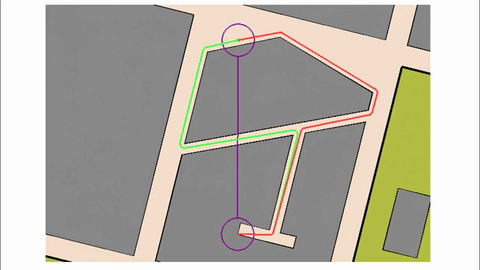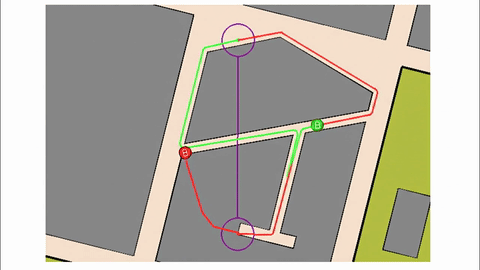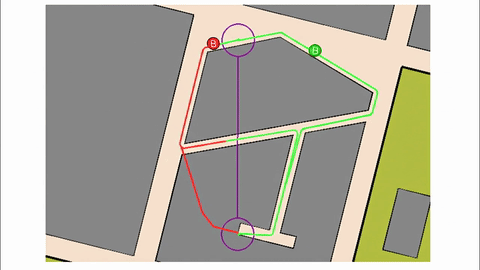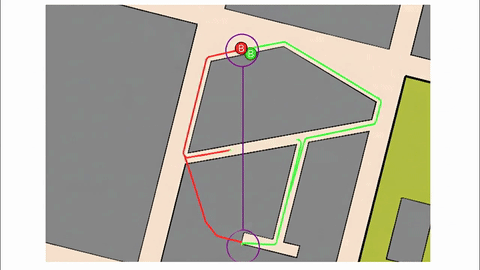
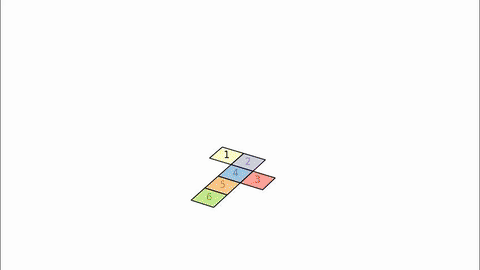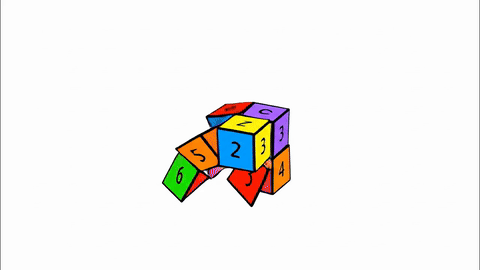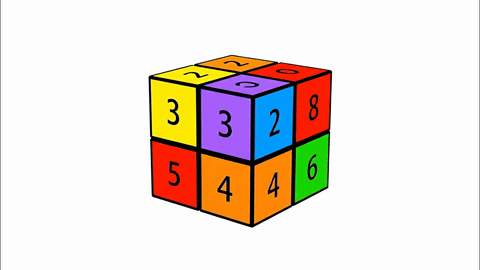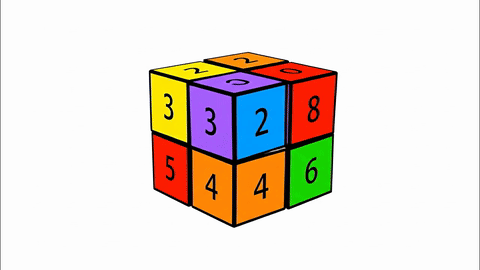
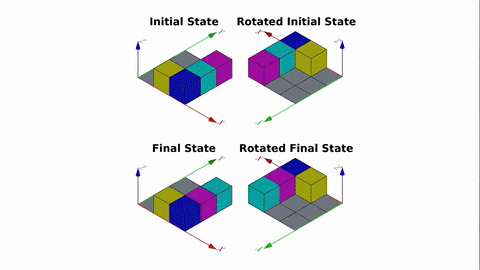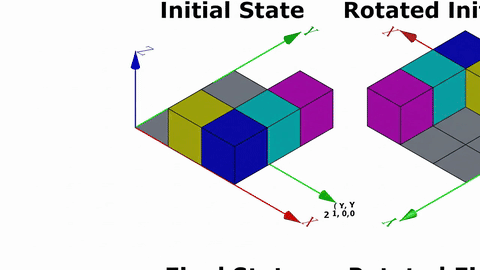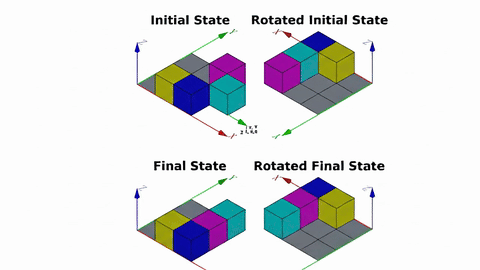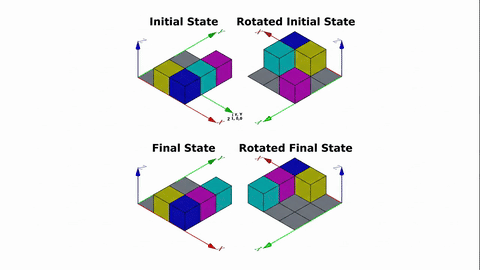
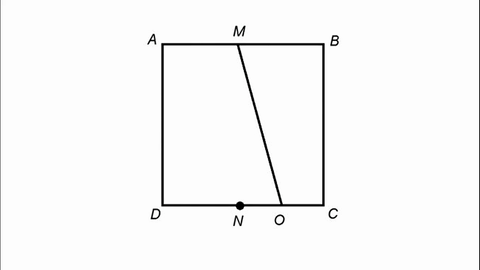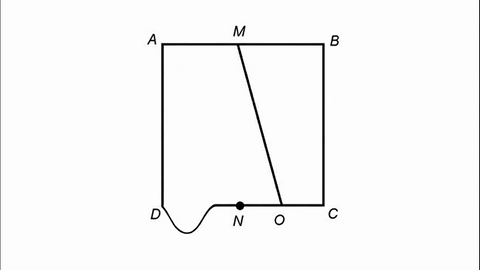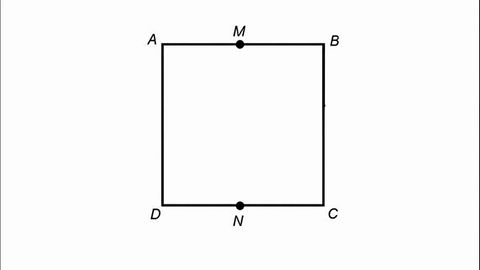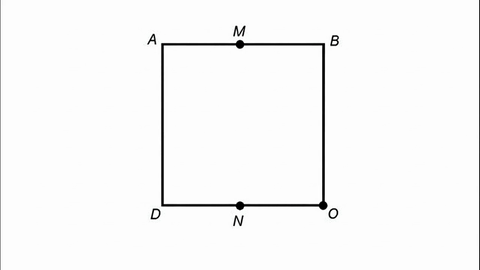
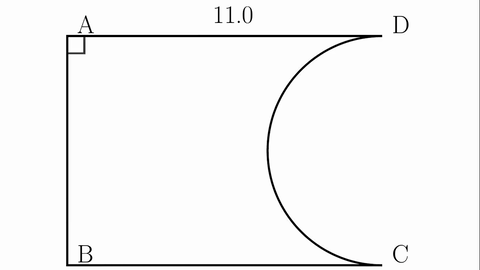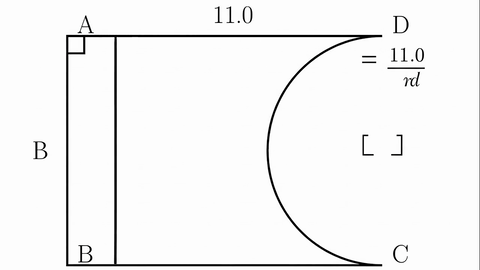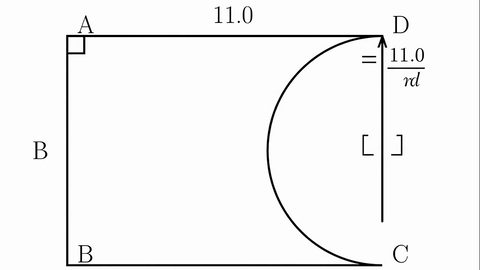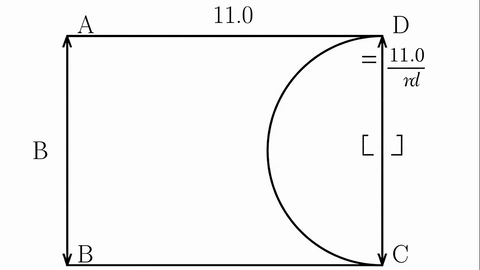
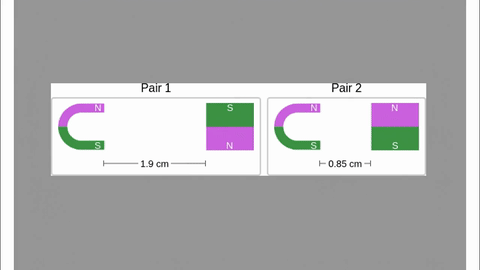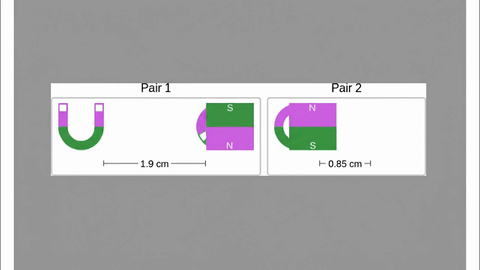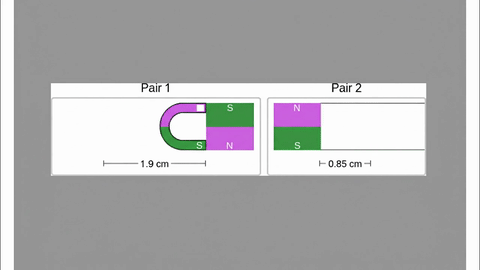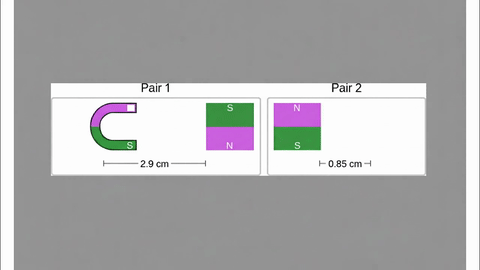
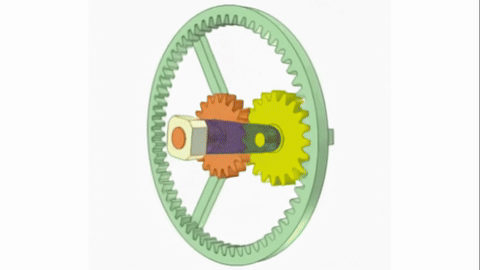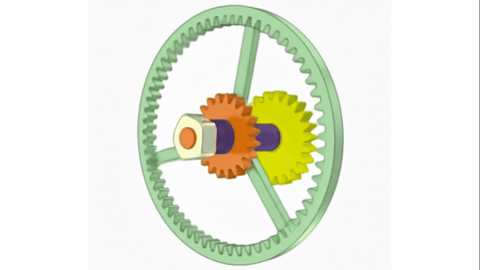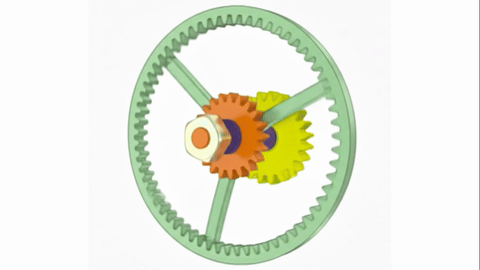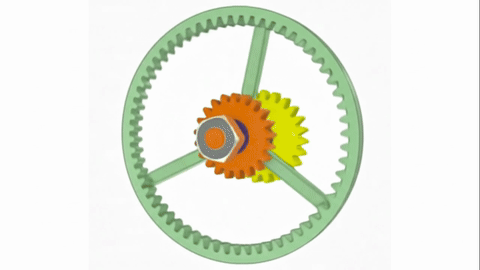
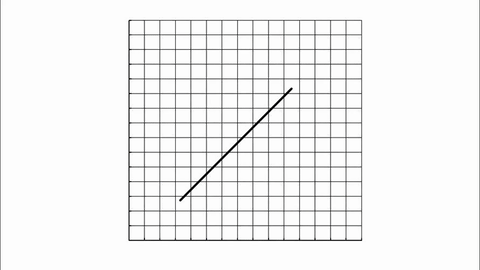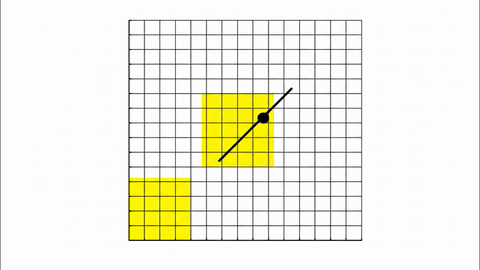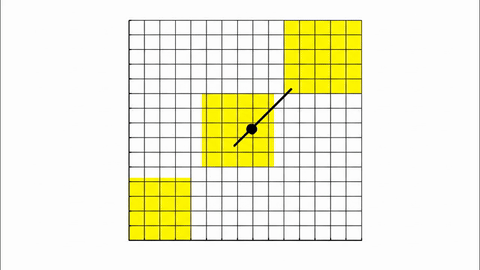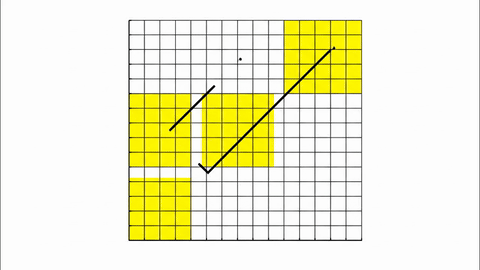
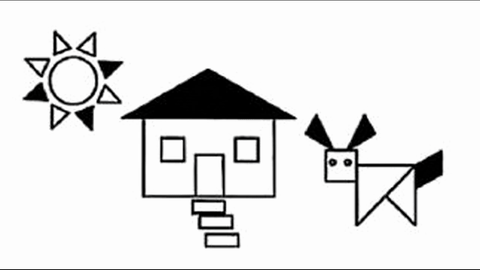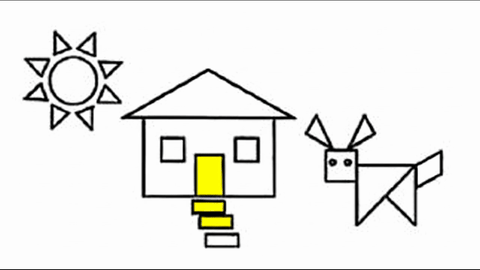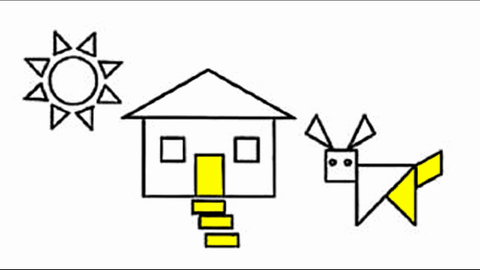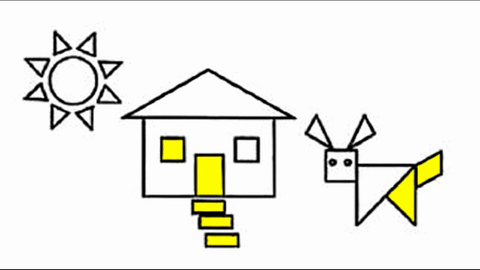
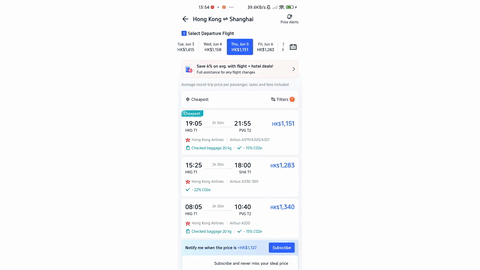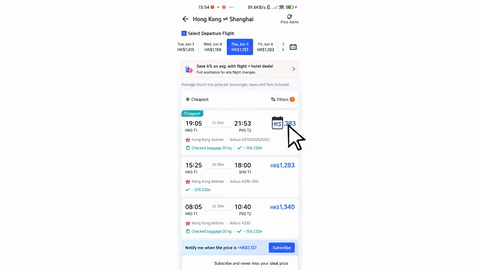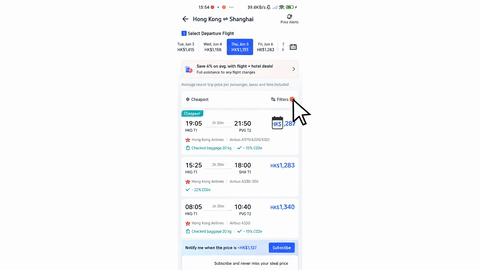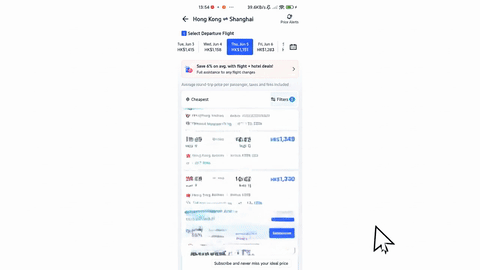
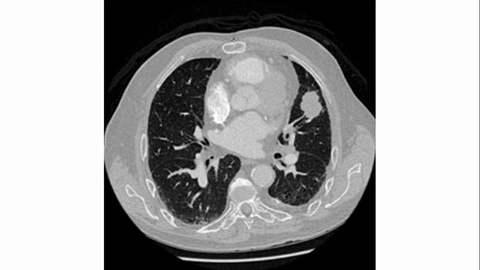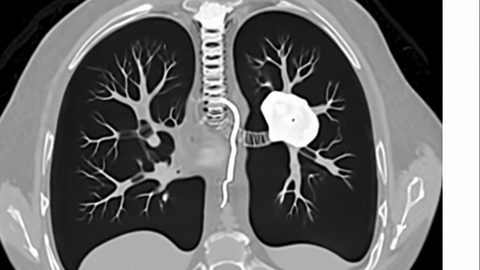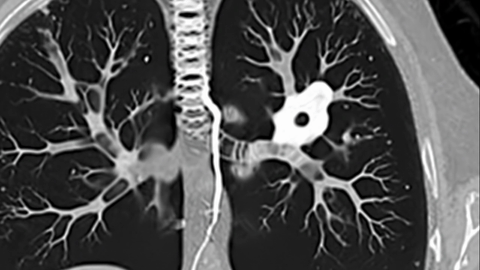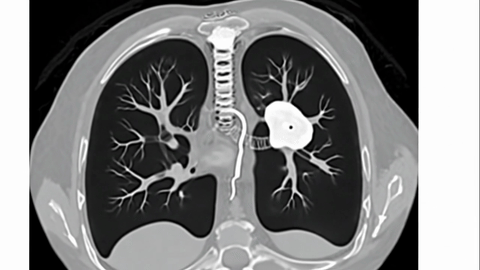
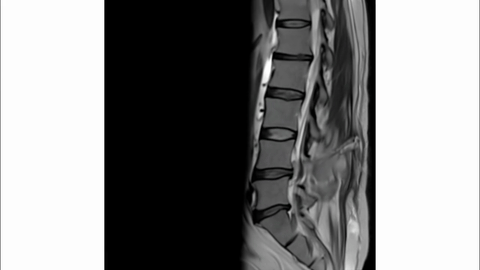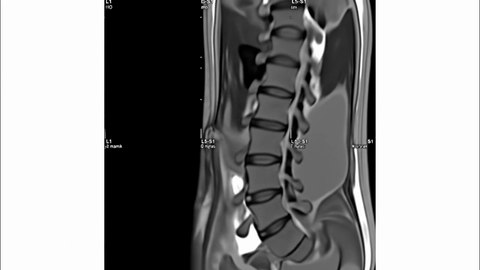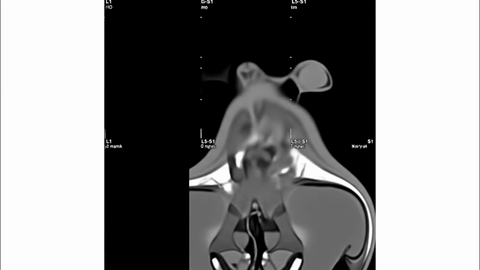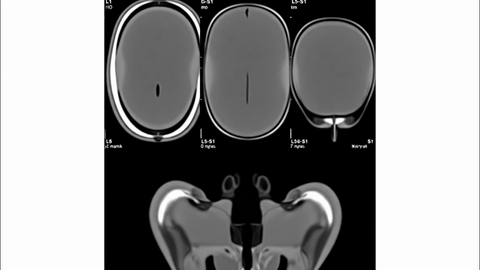
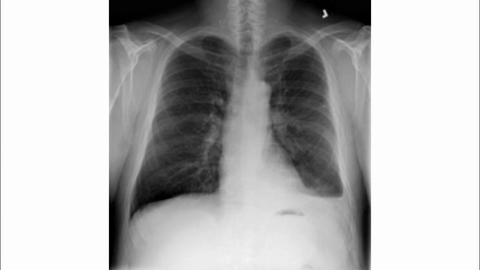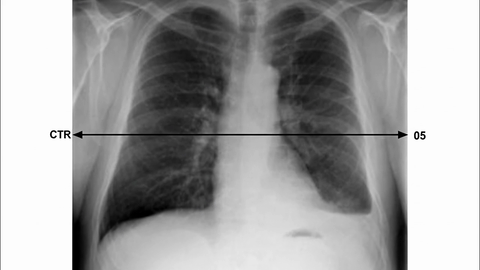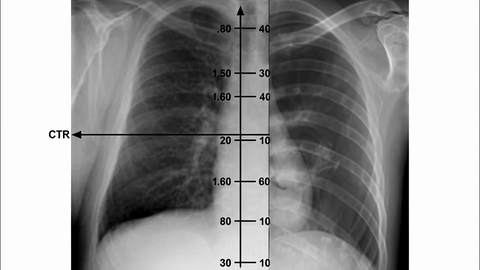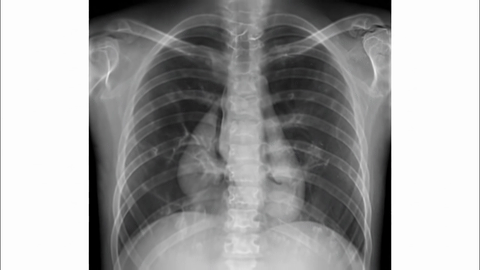
Veo-3 performs well in fine-grained attribute and spatial reasoning for salient, well-grounded targets, but fails when objects are small, occluded, or cluttered. It sometimes exhibits stylistic generation biases that lead to plausible yet instruction-divergent outcomes.
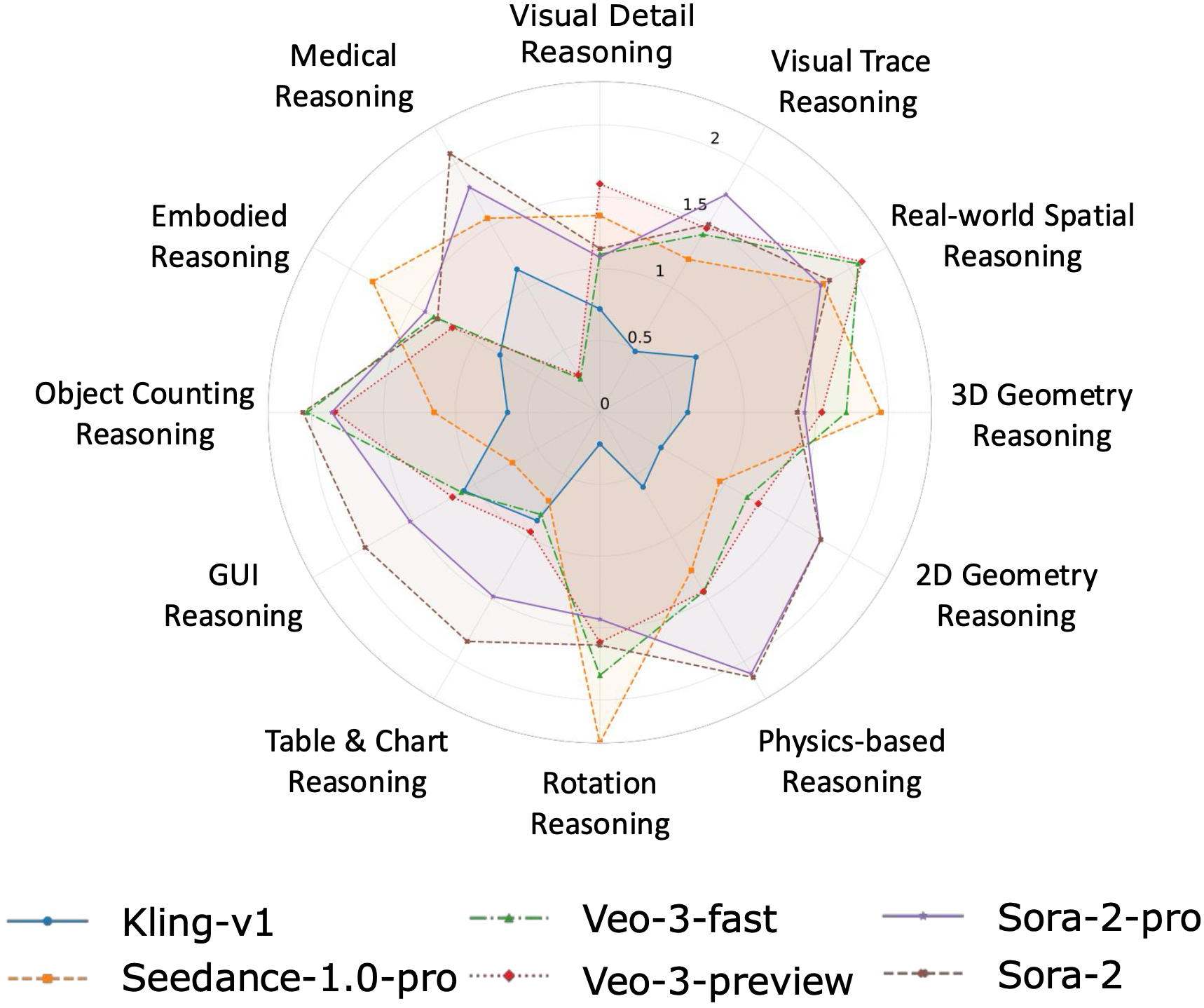
Model-level Overall and Per-dimension Performance on MME-CoF. Mean scores and standard deviations are reported on a 0–4 scale, as graded by Gemini-2.5-Pro.
| # | Model | Overall | Instruction Alignment |
Temporal Consistency |
Visual Stability |
Content Fidelity |
Focus Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kling-v1 | 0.64 ± 0.91 | 0.01 ± 0.09 | 0.15 ± 0.75 | 2.43 ± 1.86 | 0.21 ± 0.79 | 0.43 ± 1.07 |
| 2 | Seedance-1.0-pro | 1.41 ± 1.51 | 0.30 ± 0.86 | 1.65 ± 1.57 | 2.00 ± 1.72 | 1.13 ± 1.65 | 1.98 ± 1.75 |
| 3 | Veo-3.0-fast | 1.44 ± 1.51 | 0.56 ± 1.09 | 1.37 ± 1.51 | 1.88 ± 1.73 | 1.10 ± 1.52 | 2.27 ± 1.69 |
| 4 | Veo-3.0-preview | 1.45 ± 1.50 | 0.54 ± 1.06 | 1.43 ± 1.53 | 1.89 ± 1.71 | 1.12 ± 1.49 | 2.26 ± 1.73 |
| 5 | Sora-2-pro | 1.66 ± 1.53 | 0.48 ± 0.96 | 1.36 ± 1.59 | 2.39 ± 1.65 | 1.64 ± 1.72 | 2.44 ± 1.73 |
| 6 | Sora-2 | 1.72 ± 1.59 | 0.59 ± 1.12 | 1.52 ± 1.69 | 2.32 ± 1.68 | 1.62 ± 1.75 | 2.52 ± 1.71 |